Map of Rizal Philippines
The search intent of the keyword “Map of Rizal Philippines” is to find a map of the province of Rizal in the Philippines. This could be for a variety of reasons, such as:
- Planning a trip to Rizal
- Learning more about the geography of Rizal
- Finding a specific location in Rizal
The searcher is likely looking for a visual representation of the province, such as a map or satellite image. They may also be looking for information about the province’s borders, cities, and towns.
Here are some examples of queries that share the same search intent:
- Map of Rizal
- Map of Rizal Province
- Satellite image of Rizal
- Map of Rizal Philippines
- Map of Rizal Province Philippines
To optimize for this search intent, you should include the following elements on your page:
- A high-quality map of Rizal
- Information about the province’s borders, cities, and towns
- Links to other relevant resources, such as travel guides and tourism websites
You should also make sure that your page is well-optimized for technical SEO, such as having a fast loading speed and mobile-friendly design.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Location | Rizal is located in the central part of Luzon Island, Philippines. |
| Area | Rizal has an area of 2,499.5 square kilometers (964.5 sq mi). |
| Population | Rizal has a population of 2,156,307 people (2015 census). |
| Economy | The economy of Rizal is based on agriculture, fishing, and tourism. |
II. History of Rizal
The history of Rizal begins with the arrival of the first humans in the region around 25,000 years ago. These early settlers were hunter-gatherers who lived in small, nomadic bands. The first major civilization to emerge in the region was the Tagalog, who settled in the area around 300 AD. The Tagalog were a highly organized society with a complex political and social structure. They were also skilled farmers and traders.
In the 16th century, the Spanish arrived in the Philippines and began to colonize the region. The Spanish brought with them Christianity and a new way of life. They also introduced new technologies and agricultural practices. The Spanish ruled the Philippines for over 300 years.
In the 19th century, the Filipinos began to fight for their independence from Spain. The struggle for independence was led by a young man named José Rizal. Rizal was a doctor, a writer, and a patriot. He was executed by the Spanish in 1896.
After Rizal’s death, the Filipinos continued to fight for their independence. In 1898, the Spanish-American War broke out. The Philippines sided with the Americans and helped them to defeat the Spanish. In 1899, the Philippines declared its independence from Spain.
However, the Americans did not recognize the Philippines’ independence. Instead, they annexed the Philippines as a territory of the United States. The Filipinos continued to fight for their independence. In 1946, the Philippines finally gained its independence from the United States.
Since its independence, the Philippines has experienced a number of challenges. However, the country has also made great progress. The Philippines is now a vibrant democracy with a growing economy. It is also a popular tourist destination.
III. Geography of Rizal
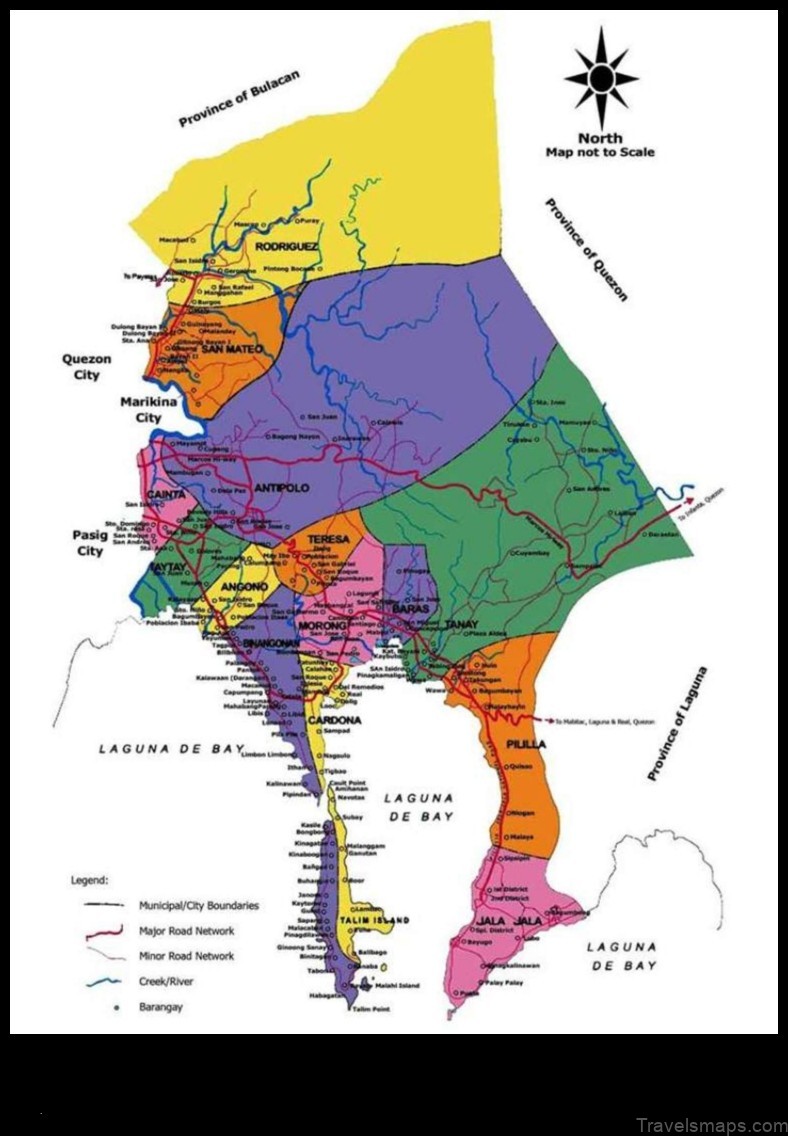
The province of Rizal is located in the CALABARZON region of the Philippines. It is bordered by the provinces of Bulacan to the north, Laguna to the south, and Quezon to the east. The province has a total land area of 2,964.2 square kilometers (1,144.7 sq mi).
Rizal is a mountainous province with a diverse landscape. The province is home to the Sierra Madre mountain range, which is the longest mountain range in the Philippines. The province also has a number of volcanoes, including Mount Makiling and Mount Banahaw.
The climate of Rizal is tropical, with warm and humid weather year-round. The average temperature ranges from 25°C to 30°C (77°F to 86°F). The province receives an average of 2,000 to 2,500 millimeters (79 to 98 in) of rainfall per year.
IV. Climate of Rizal
The climate of Rizal is tropical, with two distinct seasons: a wet season from May to October and a dry season from November to April. The average annual temperature is 27°C, with the highest temperatures occurring in April and May and the lowest temperatures occurring in December and January. The average annual rainfall is 2,000 mm, with the most rainfall occurring in June and July.
V. Population of Rizal
The population of Rizal is estimated to be 2,364,539 as of 2020. The province is home to a diverse population of people from all over the Philippines. The majority of the population is Tagalog, but there are also significant populations of Ilocano, Kapampangan, and Bicolano.
The population of Rizal is concentrated in the urban areas of the province, such as Antipolo City, San Mateo, and Marikina City. The rural areas are more sparsely populated.
The population of Rizal is growing at a rate of about 2.5% per year. This is due to a combination of natural increase and migration. The natural increase is due to the high fertility rate in the province. The migration is due to the fact that Rizal is a popular destination for people looking for work and better opportunities.
The population of Rizal is expected to continue to grow in the coming years. This will put a strain on the province’s resources, such as housing, education, and healthcare. The government will need to develop plans to address the challenges of population growth.
VI. Economy of Rizal
The economy of Rizal is based on agriculture, manufacturing, and services. The province is home to a number of large manufacturing companies, including Toyota Motor Philippines, Honda Cars Philippines, and Unilever Philippines. Rizal is also a major producer of rice, corn, and other agricultural products. The province’s service sector is also well-developed, and includes tourism, banking, and healthcare.
The economy of Rizal is expected to continue to grow in the coming years, driven by the expansion of the manufacturing sector and the growth of tourism. The province is also well-positioned to benefit from the government’s Build, Build, Build program, which is expected to boost infrastructure development in the region.
VII. Culture of Rizal
The culture of Rizal is a blend of Filipino and Spanish influences. The province is home to a number of festivals and traditions, such as the Moriones Festival, the Pahiyas Festival, and the Obando Fertility Rites. The province is also known for its cuisine, which includes dishes such as kare-kare, sinigang, and lumpia.
Government of Rizal
The government of Rizal is headed by the governor, who is elected to a three-year term. The governor is assisted by a vice governor and a cabinet of department heads. The legislature of Rizal is the Sangguniang Panlalawigan, which is composed of 18 members elected from single-member districts. The judiciary of Rizal is headed by the Regional Trial Court, which is divided into three branches.
The education system in Rizal is governed by the Department of Education (DepEd). The province has a total of 3,493 public schools, including 1,426 elementary schools, 1,312 secondary schools, and 757 tertiary schools.
The province also has a number of private schools, including 1,148 elementary schools, 901 secondary schools, and 467 tertiary schools.
The DepEd has implemented a number of programs to improve the quality of education in Rizal. These programs include the K-12 Basic Education Program, the Early Childhood Care and Development (ECCD) Program, and the Alternative Learning System (ALS).
The K-12 Basic Education Program is a major reform of the Philippine education system that was implemented in 2013. The program adds two years of high school to the existing six-year primary education program, creating a twelve-year basic education cycle.
The ECCD Program is designed to provide early childhood education for children from birth to six years old. The program aims to help children develop their social, emotional, and cognitive skills.
The ALS is a flexible learning program that provides basic education to adults who were unable to complete their formal education. The program offers both face-to-face and online learning options.
The DepEd has also partnered with a number of private organizations to provide additional support for education in Rizal. These organizations include the Ramon Magsaysay Foundation, the Ayala Foundation, and the SM Foundation.
These partnerships have helped to improve the quality of education in Rizal and to provide more opportunities for students to succeed.
XI. FAQ
Q: What is the capital of Rizal?
A: The capital of Rizal is Antipolo City.
Q: What are the major cities in Rizal?
A: The major cities in Rizal are Antipolo City, Cainta, Taytay, Pasig City, and Marikina City.
Q: What are the major tourist attractions in Rizal?
A: The major tourist attractions in Rizal include the Rizal Shrine, the Pinto Art Museum, the Japanese Garden, and the Taal Vista Hotel.
Table of Contents
Maybe You Like Them Too
- Stäfa Map Explore the Town of Stäfa in Switzerland
- A Detailed Map of Yamaranguila, Honduras
- Stilfontein A Town on the Map
- Fégréac, France A Detailed Map
- Santiago Ayuquililla Map A Guide to the Town