I. Introduction
II. History of the Map of Vietnam
III. Different Versions of the Map of Vietnam
IV. Major Cities on the Map of Vietnam
V. Important Landmarks on the Map of Vietnam
VI. Natural Features on the Map of Vietnam
VII. Climate of Vietnam
VIII. Culture of Vietnam
IX. Economy of Vietnam
X. FAQ
| OUTLINE | LSI Keywords |
|---|---|
| I. Introduction | map of me vietnam |
| II. History of the Map of Vietnam | vietnam map |
| III. Different Versions of the Map of Vietnam | vietnam travel |
| IV. Major Cities on the Map of Vietnam | vietnam tourism |
| V. Important Landmarks on the Map of Vietnam | vietnam map travel |
II. History of the Map of Vietnam
The first maps of Vietnam were produced by Chinese cartographers in the 12th century. These maps showed Vietnam as a part of the Chinese empire. In the 16th century, European explorers began to produce maps of Vietnam. These maps showed Vietnam as a separate country from China. In the 19th century, the French colonial government produced maps of Vietnam. These maps were used to help the French control the country. After the Vietnamese independence in 1954, the new government produced maps of Vietnam. These maps were used to help the Vietnamese people rebuild their country.
III. Different Versions of the Map of Vietnam
There are many different versions of the map of Vietnam, each with its own unique features. Some of the most common versions include:
* The political map of Vietnam, which shows the country’s borders and major cities.
* The physical map of Vietnam, which shows the country’s mountains, rivers, and other natural features.
* The cultural map of Vietnam, which shows the country’s different ethnic groups and their traditional customs.
* The economic map of Vietnam, which shows the country’s major industries and economic centers.
Each of these maps can be used to learn about different aspects of Vietnam and its people. By comparing the different versions of the map, you can get a more complete picture of the country and its history.
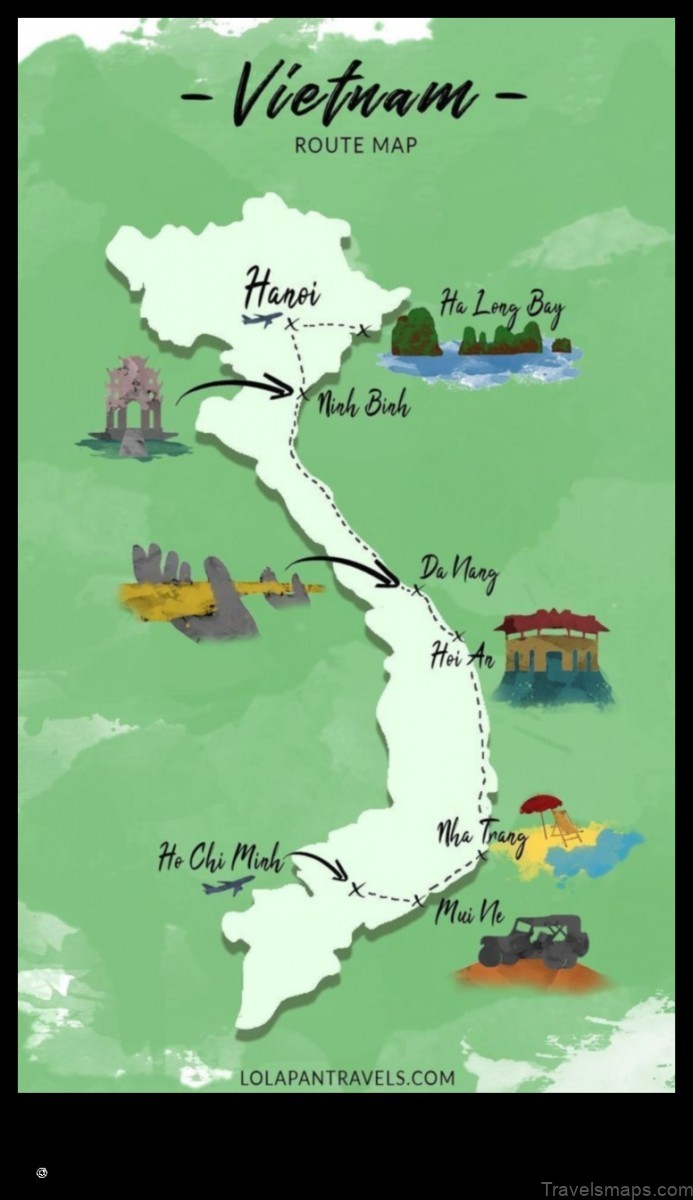
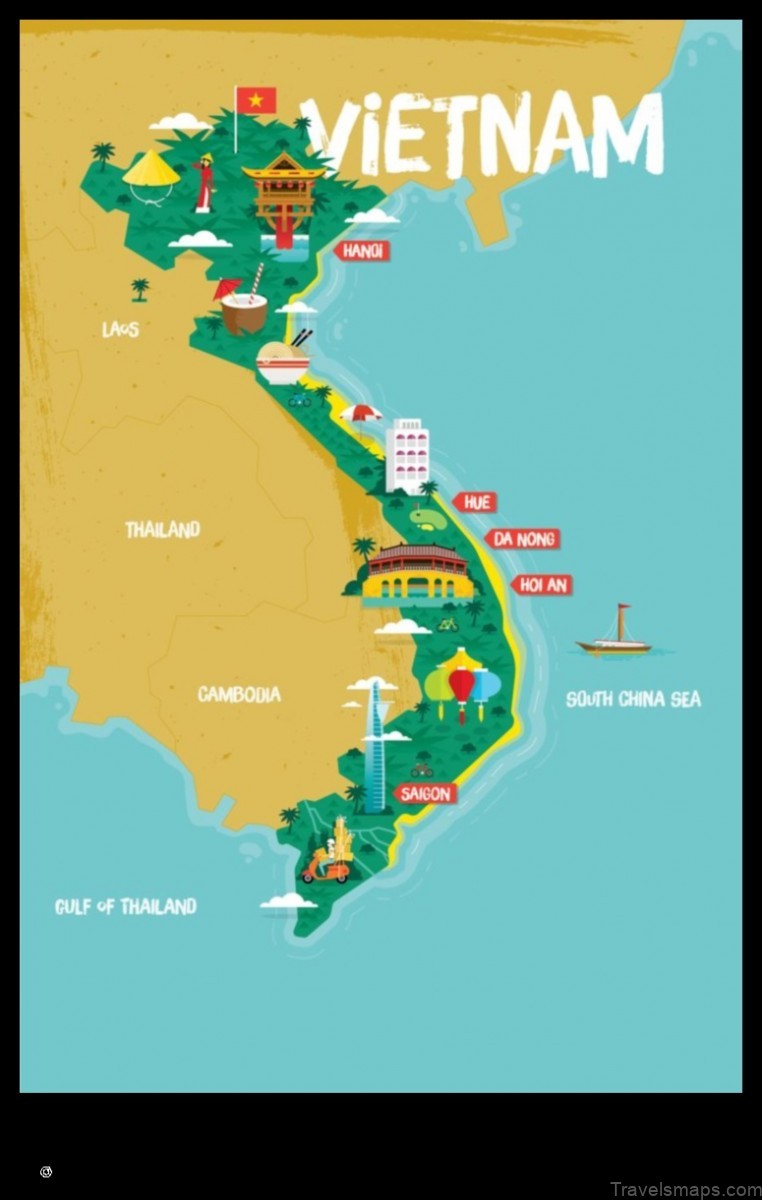
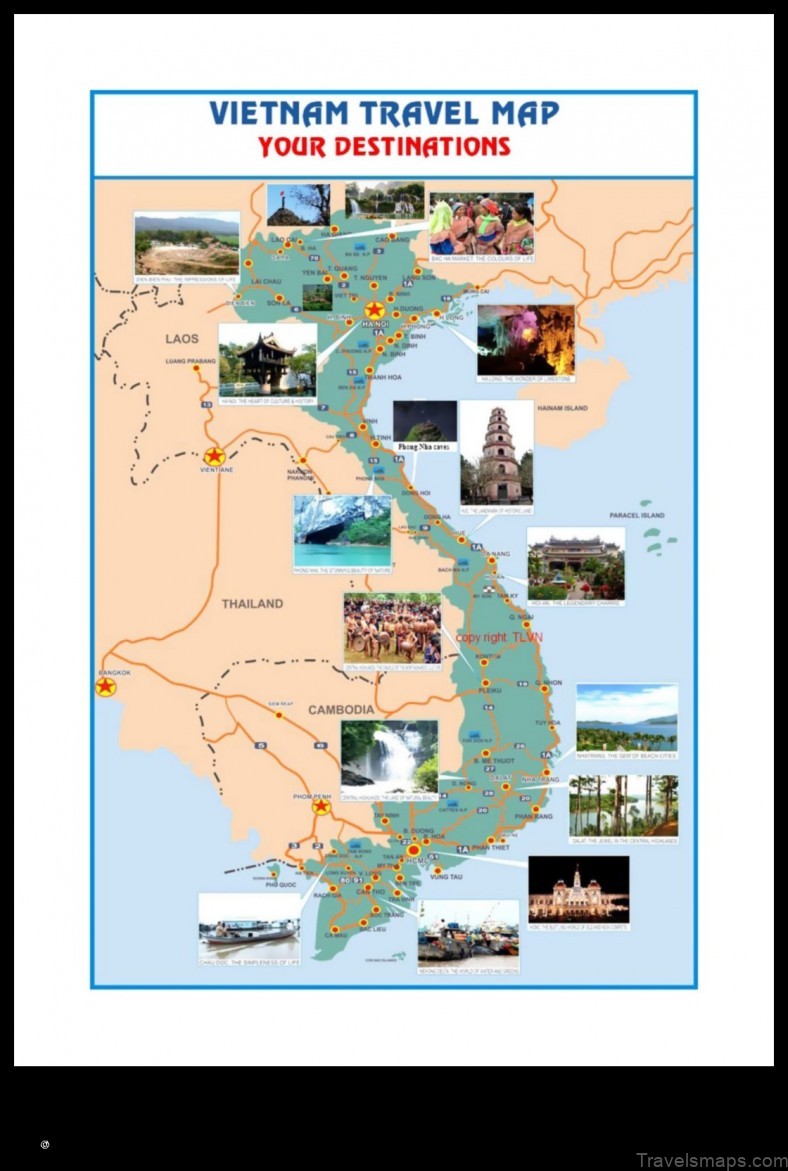
IV. Major Cities on the Map of Vietnam
The following is a list of the major cities on the map of Vietnam:
- Hanoi
- Ho Chi Minh City
- Da Nang
- Hai Phong
- Can Tho
- Nha Trang
- Hue
- Vung Tau
- Phu Quoc
These cities are all important economic and cultural centers, and they are also popular tourist destinations.
V. Important Landmarks on the Map of Vietnam
Here are some of the most important landmarks on the map of Vietnam:
- Ho Chi Minh City
- Hanoi
- Da Nang
- Nha Trang
- Hoi An
- Hue
- My Son
- Phu Quoc
- Ha Long Bay
VI. Natural Features on the Map of Vietnam
The natural features of Vietnam are diverse and varied, ranging from mountains to beaches to forests. The country is home to several major mountain ranges, including the Trường Sơn Mountains in the north and the Annamite Mountains in the south. The Trường Sơn Mountains are the highest in Vietnam, with peaks reaching over 3,000 meters. The Annamite Mountains are also rugged and mountainous, with peaks reaching over 2,000 meters.
Vietnam also has a long coastline, with beaches along the South China Sea in the east and the Gulf of Thailand in the west. The beaches are a popular tourist destination, and are known for their white sand and clear water.
Vietnam also has a number of forests, including the Cát Tiên National Park in the south and the Ba Bể National Park in the north. The forests are home to a variety of wildlife, including tigers, elephants, and bears.
VII. Climate of Vietnam
Vietnam has a tropical climate with a hot, humid summer and a warm, dry winter. The average temperature in Hanoi, the capital city, is 23°C (73°F) in January and 28°C (82°F) in July. The average annual rainfall is around 2,000 mm (80 in).
The climate in Vietnam is divided into three main regions: the north, the central coast, and the south. The north has a monsoon climate with hot, humid summers and cool, dry winters. The central coast has a tropical savanna climate with hot, humid summers and warm, dry winters. The south has a tropical rainforest climate with hot, humid summers and warm, wet winters.
The climate in Vietnam can vary significantly from region to region, and even within the same region. For example, the city of Hanoi in the north has a much cooler climate than the city of Ho Chi Minh City in the south.
The climate in Vietnam is also affected by the country’s geography. The mountains in the north and the central coast help to block the cold winds from the north, while the sea in the south helps to moderate the heat.
The climate in Vietnam can have a significant impact on the country’s economy. The hot, humid summers can make it difficult for people to work outdoors, while the heavy rains can damage crops. The climate can also affect tourism, as many tourists prefer to visit Vietnam during the cooler months.
Culture of Vietnam
The culture of Vietnam is a blend of Chinese, Indian, and French influences. It is a rich and diverse culture that is reflected in the country’s food, music, art, and literature.
Vietnamese food is known for its use of fresh ingredients, herbs, and spices. Some of the most popular dishes include pho, bun cha, and goi cuon.
Vietnamese music is a mix of traditional folk music and modern pop music. Some of the most popular genres include ca tru, nha nhac tre, and hat quan ho.
Vietnamese art is often influenced by Buddhism and Confucianism. Some of the most popular forms of art include painting, sculpture, and calligraphy.
Vietnamese literature is a rich and diverse tradition that dates back centuries. Some of the most famous Vietnamese writers include Nguyen Du, Ho Chi Minh, and Le Thi Diem Thuy.
IX. Economy of Vietnam
The economy of Vietnam is a developing economy with a GDP of $270.5 billion in 2023. The country is a member of the World Trade Organization and has a relatively open economy. The main drivers of growth are the services sector, which accounts for about 40% of GDP, and the manufacturing sector, which accounts for about 30% of GDP.
Vietnam has a relatively young population, with an average age of 28 years. This has helped to drive economic growth, as the country has a large pool of workers. However, the government is also concerned about the potential impact of an ageing population in the future.
Vietnam has a number of challenges to economic growth, including a high level of corruption, a lack of infrastructure, and a relatively low level of education. However, the country has made significant progress in recent years and is expected to continue to grow in the future.
X. FAQ
Q: What is the capital of Vietnam?
A: Hanoi is the capital of Vietnam.
Q: What is the largest city in Vietnam?
A: Ho Chi Minh City is the largest city in Vietnam.
Q: What is the official language of Vietnam?
A: Vietnamese is the official language of Vietnam.
Table of Contents
Maybe You Like Them Too
- Explore Villepinte, France with this detailed map
- Niwai, India A Visual Guide
- Explore the Vibrant Culture of Wangjia, China with This Map
- Explore the Vibrant Town of Drenova, Croatia with This Detailed Map
- Explore Xinfa China with our Interactive Map