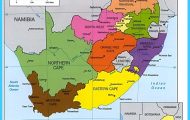
The search intent of the keyword “Map of See Austria” is informational. People who search for this keyword are looking for a map of the Austrian lake district, which is a popular tourist destination. They may be interested in finding out where the different lakes are located, how to get there, and what activities are available in the area.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Austria | A landlocked country in Central Europe |
| Map | A graphical representation of a geographical area |
| See | A body of water |
| Travel | The act of moving from one place to another |
| Vienna | The capital and largest city of Austria |
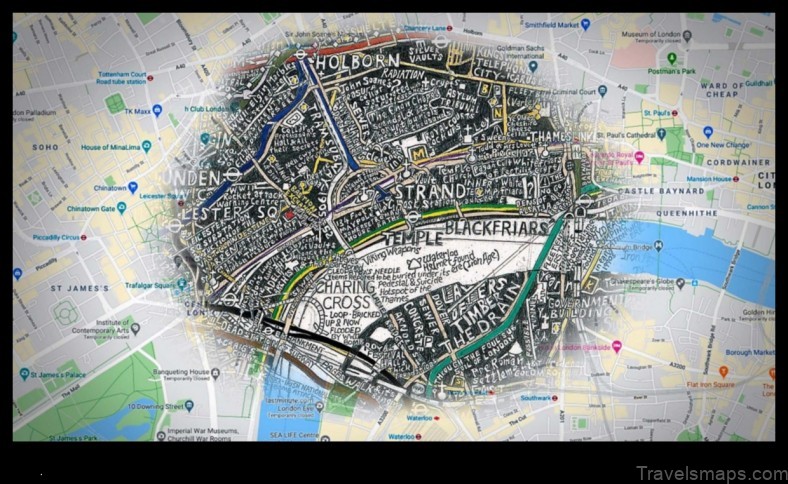
II. What is a map?
A map is a graphic representation of a geographic area, such as a country, region, or city. Maps are used to show the location of features, such as roads, rivers, and buildings. They can also be used to show elevation, climate, and other information.
Maps have been used for centuries to help people navigate the world. In ancient times, maps were often drawn on scrolls or animal skins. Today, maps are more commonly found in books, magazines, and on the internet.
Maps are an essential tool for travelers, explorers, and anyone else who needs to know where they are and how to get where they’re going. They can also be used for educational purposes, to learn about the geography of a particular area.
III. Different types of maps
There are many different types of maps, each designed for a specific purpose. Some of the most common types of maps include:
- Topographic maps show the physical features of a land area, such as mountains, rivers, and lakes.
- Political maps show the political boundaries of a country or region.
- Thematic maps show a specific theme, such as population density or climate.
- Road maps show the roads and highways of a particular area.
- Tourist maps show tourist attractions and other points of interest in a particular area.
The type of map you need will depend on the purpose for which you are using it. For example, if you are planning a hiking trip, you will need a topographic map that shows the elevation of the land. If you are planning a trip to a foreign country, you will need a political map that shows the borders of the countries you will be visiting.
When choosing a map, it is important to consider the scale of the map. The scale of a map refers to the relationship between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground. A large-scale map shows a small area in great detail, while a small-scale map shows a large area in less detail.
It is also important to consider the date of the map. Maps are constantly being updated to reflect changes in the landscape, so it is important to use a map that is as up-to-date as possible.

4. How to read a map
Maps are a valuable tool for navigating your surroundings, whether you’re exploring a new city or just trying to find your way around your neighborhood. But how do you read a map if you’re not used to it? Here are a few tips:
- Start by orienting yourself. Look for the north arrow, which will tell you which direction is north on the map.
- Use the scale to determine the distance between features on the map.
- Read the map legend to learn what the different symbols and colors represent.
- If you’re not sure what something means, ask a local or consult a guidebook.
With a little practice, you’ll be able to read maps like a pro in no time!
V. Using a map for navigation
Maps can be used for navigation in a variety of ways. They can be used to find your way around a city, to plan a road trip, or to navigate a foreign country. Here are some tips for using a map for navigation:
- Start by orienting yourself. Make sure you know which way is north, south, east, and west on the map. This will help you to figure out where you are and where you want to go.
- Use landmarks to help you find your way. Look for landmarks on the map that you can see in real life. This will help you to figure out where you are and where you need to go.
- Be aware of the scale of the map. The scale of a map tells you how much distance is represented by each unit of measurement on the map. This is important to know when you are trying to figure out how far you need to travel to reach your destination.
- Use a compass to help you stay on track. A compass can be a helpful tool for navigation, especially if you are traveling in an unfamiliar area.
- Don’t be afraid to ask for help. If you get lost, don’t be afraid to ask for help from a local. They may be able to give you directions or help you find your way back to your destination.
By following these tips, you can use a map to help you navigate your way around a variety of different locations.
VI. Map symbols and legends
Map symbols and legends are essential for understanding a map. They provide information about the different features that are shown on the map, such as roads, rivers, and buildings. Map symbols are usually represented by a small icon, while the legend is a key that explains what each symbol means.
Here is an example of a map legend:
As you can see, the legend provides a key to the different symbols that are used on the map. For example, the blue lines represent roads, the green lines represent rivers, and the red dots represent buildings.
It is important to read the legend carefully before you start using a map. This will help you to understand what the different symbols mean and how to use the map effectively.
VII. Map projections
A map projection is a way of representing the three-dimensional surface of the Earth on a two-dimensional surface, such as a flat piece of paper.
There are many different map projections, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The best projection for a particular map depends on the purpose of the map and the area being mapped.
Some of the most common map projections include:
- Mercator projection
- Transverse Mercator projection
- Gnomonic projection
- Azimuthal equidistant projection
- Robinson projection
Each of these projections has its own unique characteristics. For example, the Mercator projection is a conformal projection, which means that it preserves angles. This makes it a good choice for maps that will be used for navigation. However, the Mercator projection also distorts the size of objects as they get further from the equator, so it is not a good choice for maps of large areas.
The Transverse Mercator projection is a variation of the Mercator projection that is designed for maps of specific regions. It is a conformal projection, but it does not distort the size of objects as much as the Mercator projection.
The Gnomonic projection is a perspective projection, which means that it is based on the view of the Earth from a point directly above the North Pole. This projection does not preserve angles or shapes, but it does show the shortest distance between two points on the Earth’s surface.
The Azimuthal equidistant projection is a projection that shows all points on the Earth’s surface at the same distance from a central point. This projection is not conformal, but it does preserve the shape of circles.
The Robinson projection is a compromise projection that attempts to balance the distortions of the other projections. It is not conformal, but it does not distort the size of objects as much as the Mercator projection.
The choice of which map projection to use depends on the purpose of the map and the area being mapped.
History of mapsMaps have been around for centuries, and they have played an important role in human history. The earliest maps were created by ancient civilizations, such as the Egyptians and the Babylonians. These maps were often used for navigation and military purposes.
In the Middle Ages, maps became more detailed and accurate. The first world map was created by the cartographer Ptolemy in the 2nd century AD. This map was based on the work of earlier Greek and Roman geographers.
During the Renaissance, maps became even more accurate and detailed. The first printed maps were produced in the 15th century, and these maps were widely distributed. Maps were used by explorers to find new lands and by merchants to trade with other countries.
In the 19th century, maps became more scientific. The first topographic maps were created, and these maps showed the elevation of the land. In the 20th century, maps became even more accurate with the use of satellites and aerial photography.
Today, maps are used for a variety of purposes, including navigation, planning, and education. Maps are an essential tool for understanding the world around us.
IX. The future of maps
Maps have come a long way in the past few centuries, and they are still evolving today. New technologies are making it possible to create maps that are more accurate, more detailed, and more interactive than ever before.
One of the most significant trends in mapmaking is the use of satellite imagery. Satellites can provide images of the Earth’s surface that are much more detailed than traditional maps. This data can be used to create maps that show everything from the location of roads and buildings to the topography of the land.
Another trend in mapmaking is the use of 3D technology. 3D maps allow users to see a map from different angles and to zoom in on specific areas. This can be helpful for understanding the layout of a city or for planning a trip.
Finally, the increasing use of the internet is making it possible to create and share maps in new ways. Online maps can be accessed from anywhere in the world, and they can be updated in real time. This makes them a valuable tool for businesses, governments, and individuals.
The future of maps is bright. As new technologies develop, maps will become even more accurate, more detailed, and more interactive. This will make them even more useful tools for navigating the world around us.
X. FAQ
Here are three common questions about maps and their answers:
Question 1: What is the difference between a map and a globe?
Answer: A map is a flat representation of a three-dimensional surface, while a globe is a spherical representation of the Earth. Maps are used to represent different aspects of the Earth, such as its physical features, political boundaries, and climate. Globes are used to visualize the Earth’s rotation and its relationship to other planets in the solar system.
Question 2: How do you read a map?
Answer: There are a few different ways to read a map. The most common way is to use the cardinal directions (north, south, east, and west). You can also use the map’s scale to determine the distance between two points. Finally, you can use the map’s legend to identify the different symbols used to represent different features on the map.
Question 3: What are the different types of maps?
Answer: There are many different types of maps, each designed to show a specific type of information. Some of the most common types of maps include:
- Physical maps: These maps show the physical features of the Earth, such as mountains, rivers, and lakes.
- Political maps: These maps show the political boundaries of countries, states, and cities.
- Thematic maps: These maps show a specific type of information, such as population density, climate, or land use.
Table of Contents
Maybe You Like Them Too
- El Cardo A Town Map in the Heart of Andalusia
- Solwezi, Zambia A Detailed Map
- Danilovka A Tovn In Saratov Region
- Al Mushannaf, Syrian Arab Republic A Detailed Map
- MAP OF ORLEA, ROMANIA